Remote Sensing
Remote sensing involves gathering data about an object or area from a distance using technologies such as satellites or aircraft. Its applications span numerous fields, offering valuable insights and support in various domains:

Agriculture
- Crop Monitoring: Remote sensing technology is used to monitor crop health, estimate yields, and detect stress factors such as drought, pests, and diseases. This information is valuable for precision agriculture, helping farmers to optimize inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Crop Health: By assessing crop conditions and detecting pests, remote sensing helps monitor plant health using indicators like the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI).
Precision Farming: It supports targeted application of resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, enhancing efficiency and crop yields
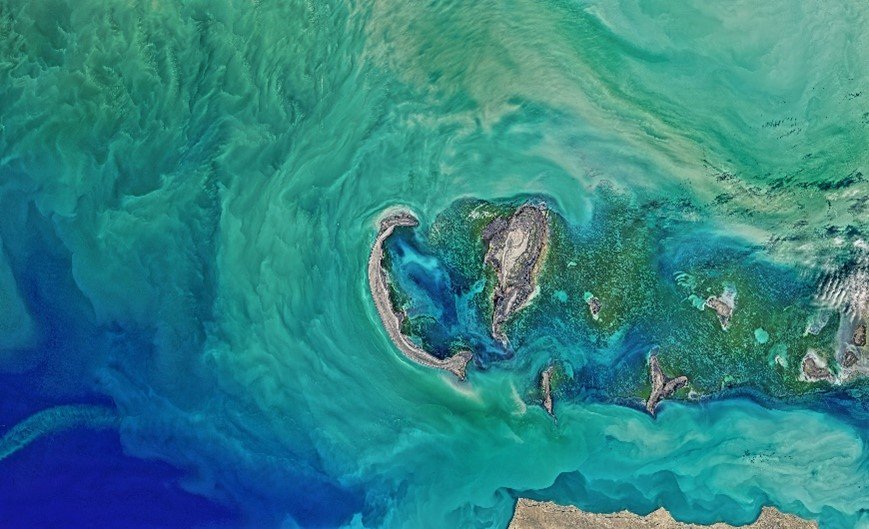

Marine and Coastal Management
- Coastal Zone Monitoring: Remote sensing is used to monitor coastal erosion, sediment transport, and changes in coastal landforms. This is vital for managing coastal resources and protecting against sea-level rise.
Marine Ecosystem Health: Satellite imagery helps in monitoring the health of coral reefs, mangroves, and other marine ecosystems. It is also used to track algal blooms and assess the impact of pollution on marine life
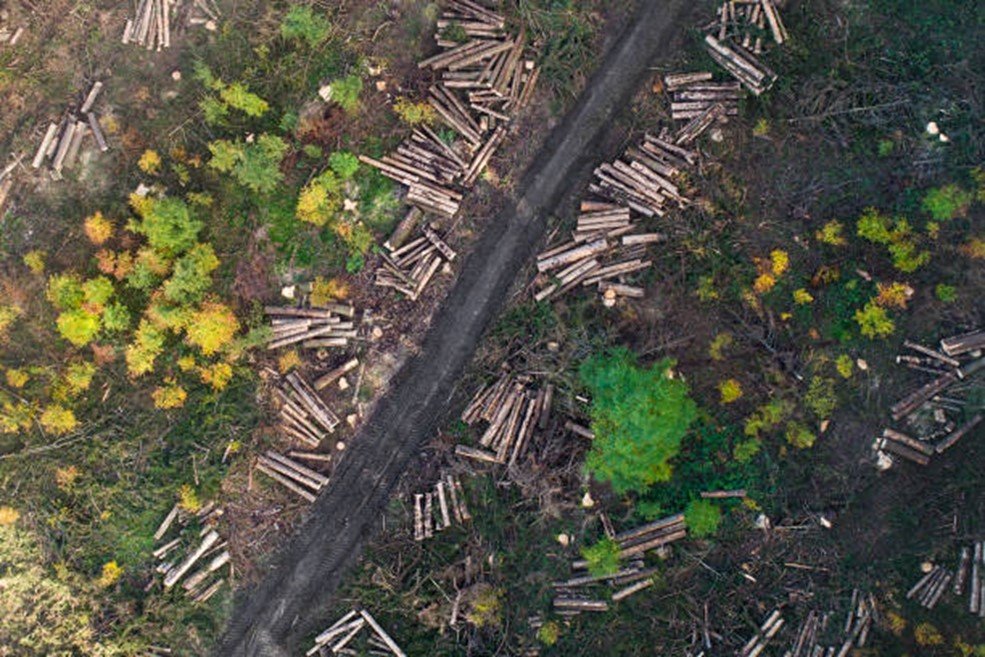

Environmental Monitoring:
- Deforestation: Remote sensing tracks changes in forest cover, helping to monitor deforestation and forest degradation over time.
- Climate Change: Satellites provide crucial data on atmospheric conditions and ice coverage, aiding climate models and the study of global warming
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health: By analyzing satellite images, researchers can monitor the health of ecosystems, track changes in vegetation, and assess the impact of deforestation, desertification, and habitat fragmentation
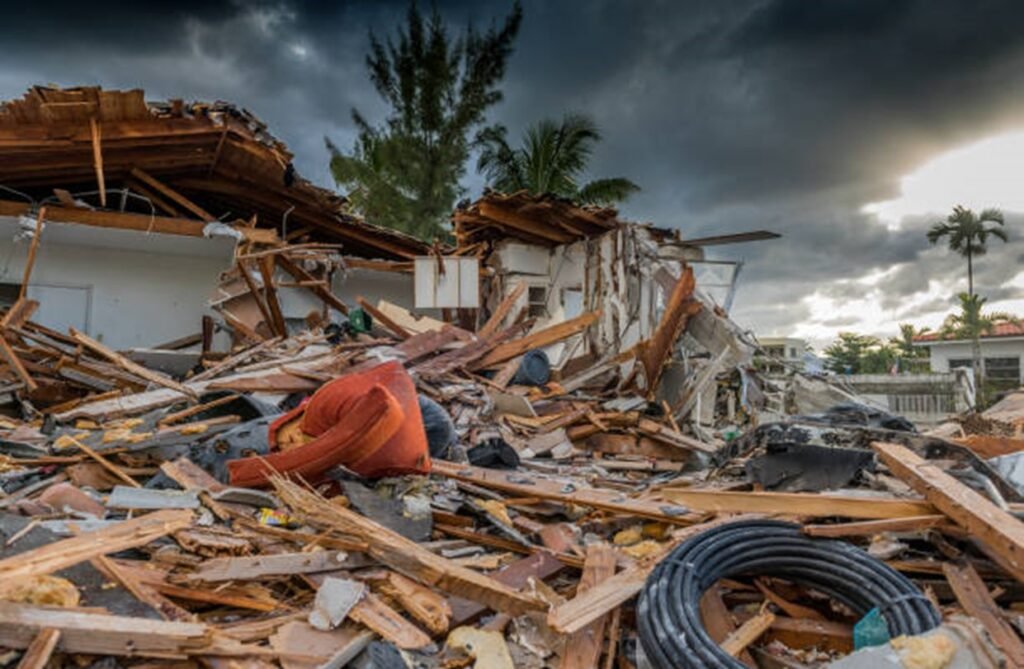

Disaster Management
- Flood and Drought Monitoring: Remote sensing is essential for monitoring and predicting natural disasters like floods and droughts. It allows for the rapid assessment of affected areas and supports emergency response efforts.
- Earthquake Damage Assessment: After an earthquake, remote sensing data can be used to assess the extent of damage to infrastructure and buildings, helping in disaster recovery planning.
Forest Fire Detection: Satellite imagery can detect and monitor wildfires in real-time, providing critical information for firefighting and evacuation efforts.
Natural Disasters: Remote sensing evaluates damage from events like earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires, assisting in emergency response and recovery.
Hazard Mapping: It helps create hazard maps to identify at-risk areas and guide disaster preparedness strategies

Urban Planning and Development:
- Land Use and Land Cover: Provides data on land use patterns for effective city planning, zoning, and infrastructure development.
- Urban Expansion: Monitors urban growth and sprawl, supporting sustainable development and resource management
- Urban Sprawl and Land Use Planning: Remote sensing provides valuable data for urban planners to monitor urban growth, assess land use changes, and plan sustainable development. It helps in managing infrastructure, transportation networks, and green spaces in rapidly expanding cities
Water Resources Management:
Water Quality: Remote sensing helps assess the quality of water bodies by detecting pollutants and monitoring changes in water conditions, such as algal blooms and sediment levels.
Hydrological Modeling: Data on precipitation, soil moisture, and land cover from remote sensing supports hydrological models that simulate river flow, watershed dynamics, and water availability. This information is crucial for water management and flood forecasting.

Infrastructure Monitoring
- Transportation Networks: Remote sensing tracks the condition of infrastructure such as roads, railways, and bridges. This helps with maintenance planning, detecting structural issues, and managing transportation systems.
- Structural Health: Techniques like radar and LiDAR are used to assess the condition of large structures, identifying signs of deterioration or damage. This information is essential for safety and repair planning.

Archaeology
- Site Discovery: Remote sensing technologies like LiDAR and multispectral imaging help uncover and map archaeological sites and features hidden beneath vegetation or soil, facilitating the discovery of ancient ruins and artifacts.
- Site Monitoring: It monitors archaeological sites to prevent damage from environmental changes or human activities. This helps preserve cultural heritage and ensures the protection of historical sites.

Defense and Security
- Surveillance: Remote sensing technologies are used for reconnaissance and monitoring of borders, conflict zones, and military facilities. High-resolution imagery and radar data enhance situational awareness and support intelligence operations.
- Disaster Response: In addition to monitoring disasters, remote sensing assists defense operations by providing situational updates, supporting logistics, and coordinating response efforts in affected areas.

Healthcare
Disease Surveillance: Remote sensing helps track environmental conditions related to vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue, by monitoring factors like rainfall and vegetation that influence disease spread.
Environmental Monitoring: Satellite data assesses air and water quality, providing critical information on pollutants and contaminants that can impact respiratory and overall health.
Disaster Response: Remote sensing quickly evaluates damage and identifies areas in need of medical aid after natural disasters, aiding in efficient response and resource allocation.
Urban Health Analysis: It helps identify urban heat islands and assess access to healthcare facilities, contributing to improved public health planning and infrastructure development.
