Mapping
Maps are graphical representations of geographic areas, illustrating spatial relationships between features such as landmarks, landscapes, and built environments. They are essential tools in various disciplines, providing critical information for decision-making, navigation, planning, and communication.
- Customized Maps
- Topographic Maps
- Thematic Maps
- Political Maps
- Physical Maps
- Climate Maps
- Economic or Resource Maps
- Road and Street Maps
- Cadastral Maps
- Historical Maps
- Interactive and Digital Maps
- Choropleth Maps
- Isoline Maps
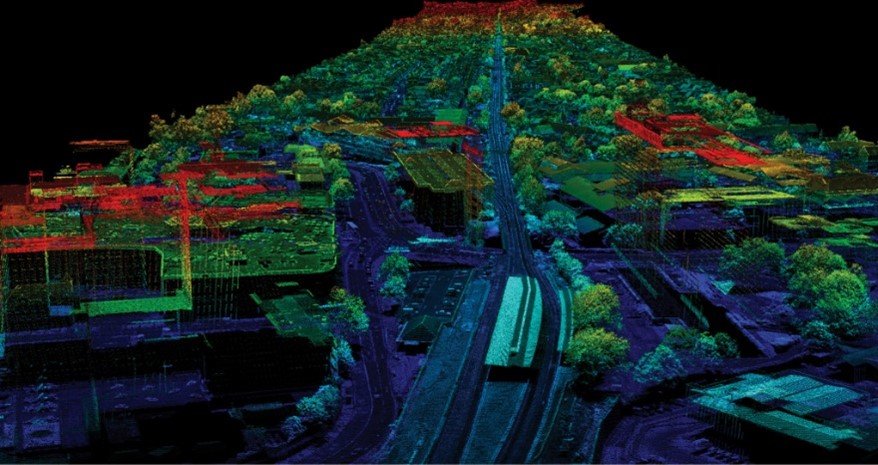

Survey
Surveying is the science and practice of measuring and mapping the Earth’s surface. It involves determining the locations of points, as well as the distances and angles between them, using a range of tools and technologies
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) Surveying
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development
- forestry management,
- flood modeling
- Agricultural Management
- Disaster Response and Recovery
- Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Mapping
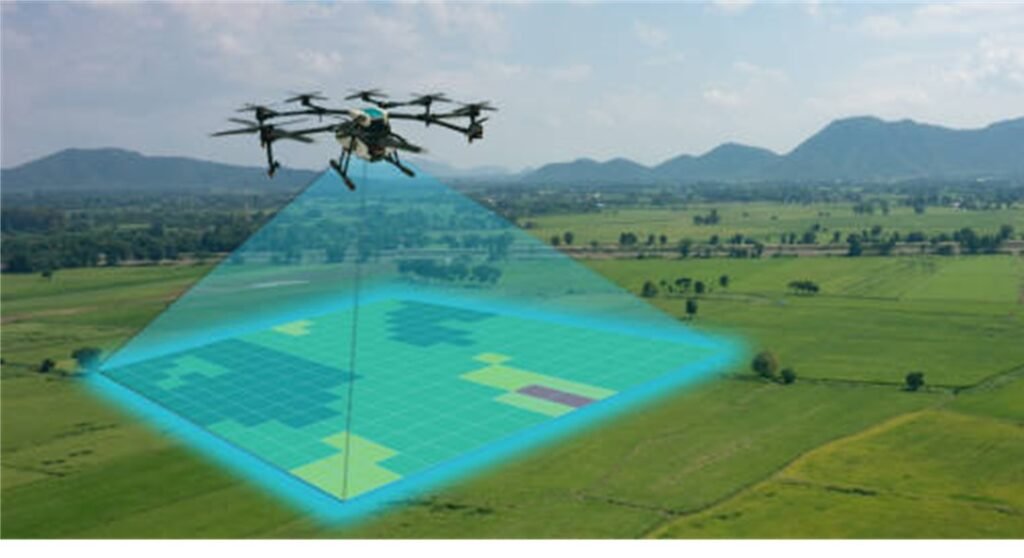

Drones (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles – UAVs)
- Infrastructure inspection
- Agriculture monitoring
- Mining and Resource Exploration
- Traffic and Transportation Analysis
- Disaster Response and Management
- Surveying and Mapping
- Cultural Heritage Preservation

Utility Surveying
- Utility Location and Mapping
- Infrastructure maintenance,
- construction planning
- Construction and Renovation Projects
- Utility Conflict Detection
- Asset Management and Maintenance
- Public Works and Municipal Services
Cadastral Surveying
- Property Boundary Definition
- Real estate transactions
- land subdivision
- property registration
- Environmental and Conservation Planning
- Public Infrastructure Projects
- Land Use and Zoning
- Legal Dispute Resolution
- Asset mapping
- Easement and Right-of-Way Management
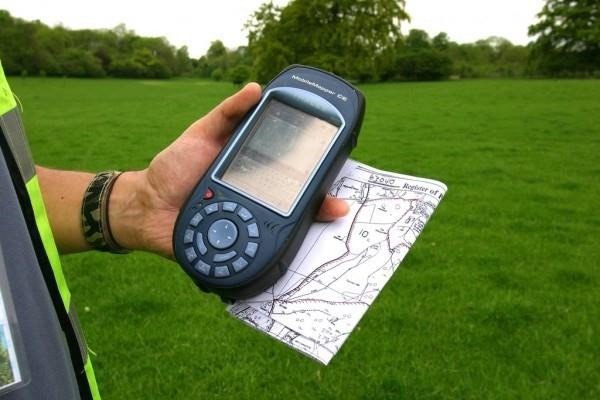

GPS Surveying
- Ideal for large-scale surveys
- Land Surveying
- mapping, and navigation
- Construction and Engineering
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Agriculture and Precision Farming
- Environmental Monitoring
- Transportation and Navigation
- Emergency Response and Management
- Utilities and Infrastructure Management
- Surveying and Mapping
- Real Estate and Property Management
- Military and Defense
- Scientific Research

Social and Demographic Surveys
- Policy and Decision Making
- Urban and Regional Planning
- Health and Social Services
- Education and Workforce Development
- Market Research and Consumer Behavior
- Election and Voting Analysis
- Social Research and Academic Studies
- Economic Development
- Community Development and Engagement
- Crisis and Emergency Response
- Migration and Demographic Changes
- Housing and Living Conditions

Topographic Survey
Land Development and Urban Planning
Construction and Engineering Projects
Environmental Management and Conservation
Flood Risk Assessment and Management
Mining and Resource Extraction
Utility and Infrastructure Planning
Land Use and Property Management
Historical and Archaeological Research
Military and Defense Operations

Defense and Security
- Surveillance: Remote sensing technologies are used for reconnaissance and monitoring of borders, conflict zones, and military facilities. High-resolution imagery and radar data enhance situational awareness and support intelligence operations.
- Disaster Response: In addition to monitoring disasters, remote sensing assists defense operations by providing situational updates, supporting logistics, and coordinating response efforts in affected areas.

Healthcare
Disease Surveillance: Remote sensing helps track environmental conditions related to vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue, by monitoring factors like rainfall and vegetation that influence disease spread.
Environmental Monitoring: Satellite data assesses air and water quality, providing critical information on pollutants and contaminants that can impact respiratory and overall health.
Disaster Response: Remote sensing quickly evaluates damage and identifies areas in need of medical aid after natural disasters, aiding in efficient response and resource allocation.
Urban Health Analysis: It helps identify urban heat islands and assess access to healthcare facilities, contributing to improved public health planning and infrastructure development.
